PAT520钻石争霸赛-2022解题报告
7-1 520表白
题目

思路
非常简单的输入输出。
题解代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<n<<"! 520!";
return 0;
}提交记录
7-2 分糖豆
题目
思路
计算分配所需的糖豆数量,然后和已知的进行对比,根据对比结果输出对应的内容即可。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N, M, K;
int need;
cin >> N >> M >> K;
need = N * K; //计算所需
if (need > M)
cout << "hai cha " << need - M << "!";
else if (need == M)
cout << "zheng hao mei ren " << K << "!";
else
cout << "hai sheng " << M - need << "!";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}提交记录

7-3 约会App
题目
思路
使用变量记录约会对象的要求,然后根据条件对每一个输入的信息进行判断即可。如果满足要求,根据格式输出数据。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int gender, age_low, age_high, hight_low, hight_high, n; //读入各项标准
cin >> gender >> age_low >> age_high >> hight_low >> hight_high >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int tg, ta, th;
cin >> tg >> ta >> th; //读入一组数据
if (tg != gender &&
ta >= age_low && ta <= age_high &&
th >= hight_low && th <= hight_high) //如果满足要求
cout << tg << " " << ta << " " << th << endl;
}
return 0;
}提交记录
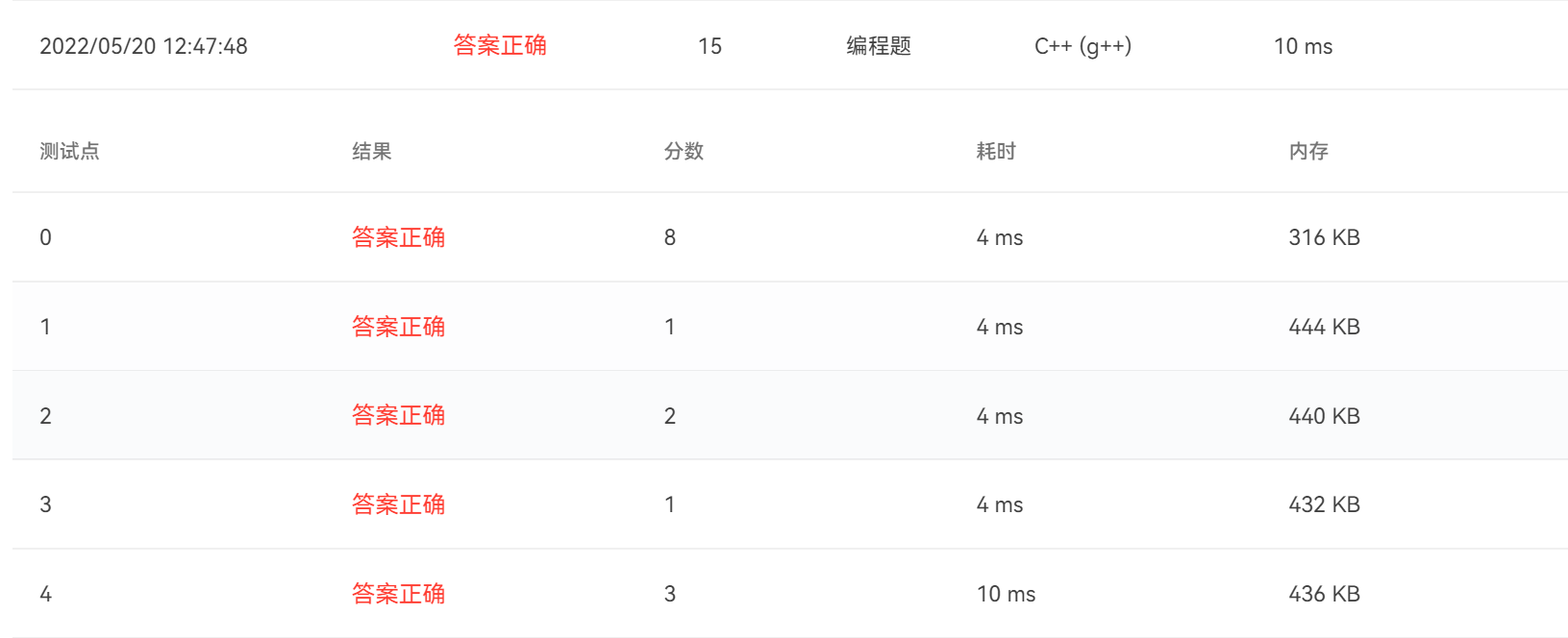
7-4 关于奇数的等式
题目
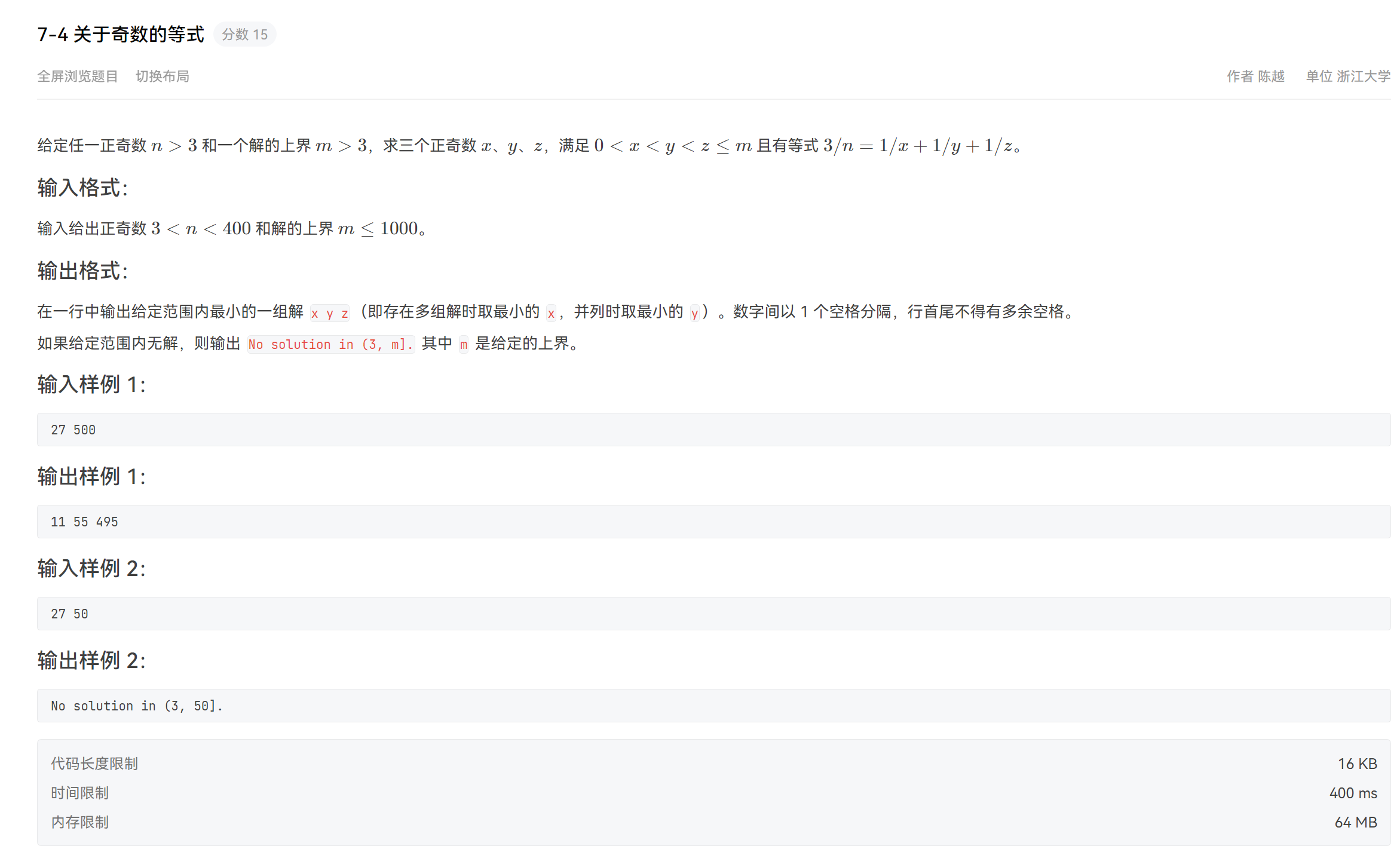
思路
根据题目给出的等式做变换,通分后变成整数的等式。然后,暴力匹配找到符合要求的(题目条件说明了是奇数所以只需要处理奇数)。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
bool find = false;
for (int x = 1; x <= m; x += 2) { //三层遍历,只处理奇数
for (int y = x + 2; y <= m; y += 2) {
for (int z = y + 2; z <= m; z += 2) {
if (3 * x * y * z == n * (x * y + x * z + y * z)) { //如果满足要求,则输出并
cout << x << " " << y << " " << z;
find = true;
break;
}
}
if (find) break;
}
if (find) break;
}
if (!find) cout << "No solution in (3, " << m << "].";
return 0;
}提交记录
7-5 我侬数
题目
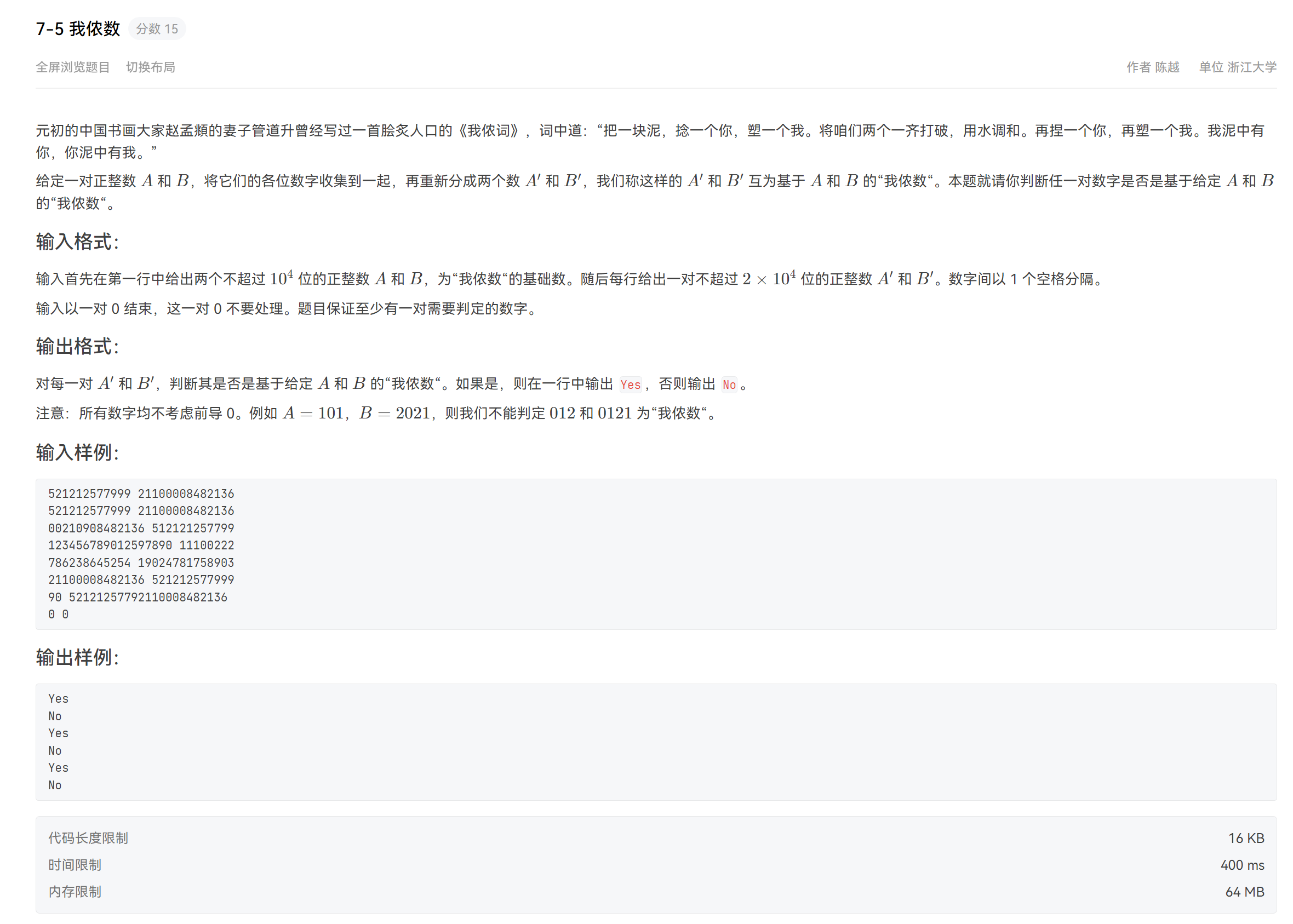
思路
这个题目其实是字符串处理,首先对基准数字去除前置0,然后剩余的转换为一个字符串并且排序(便于比对)。其他的做同样的处理后和基准字符串比对即可。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string numa, numb;
cin >> numa >> numb;
int index = 0; //处理前置0
while (numa[index] == '0') index++;
numa = numa.substr(index);
index = 0;
while (numb[index] == '0') index++;
numb = numb.substr(index);
numa += numb; //两数相加
sort(numa.begin(), numa.end()); //排序
string a, b;
while (true) {
cin >> a >> b;
if (a == "0" && b == "0") //如果遇到结束的 0 0结束循环
break;
index = 0; //去除a,b的前置0
while (a[index] == '0') index++;
a = a.substr(index);
index = 0;
while (b[index] == '0') index++;
b = b.substr(index);
a += b; //相加并排序
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
cout << (numa == a ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
return 0;
}提交记录
7-6 非诚勿扰
题目
思路
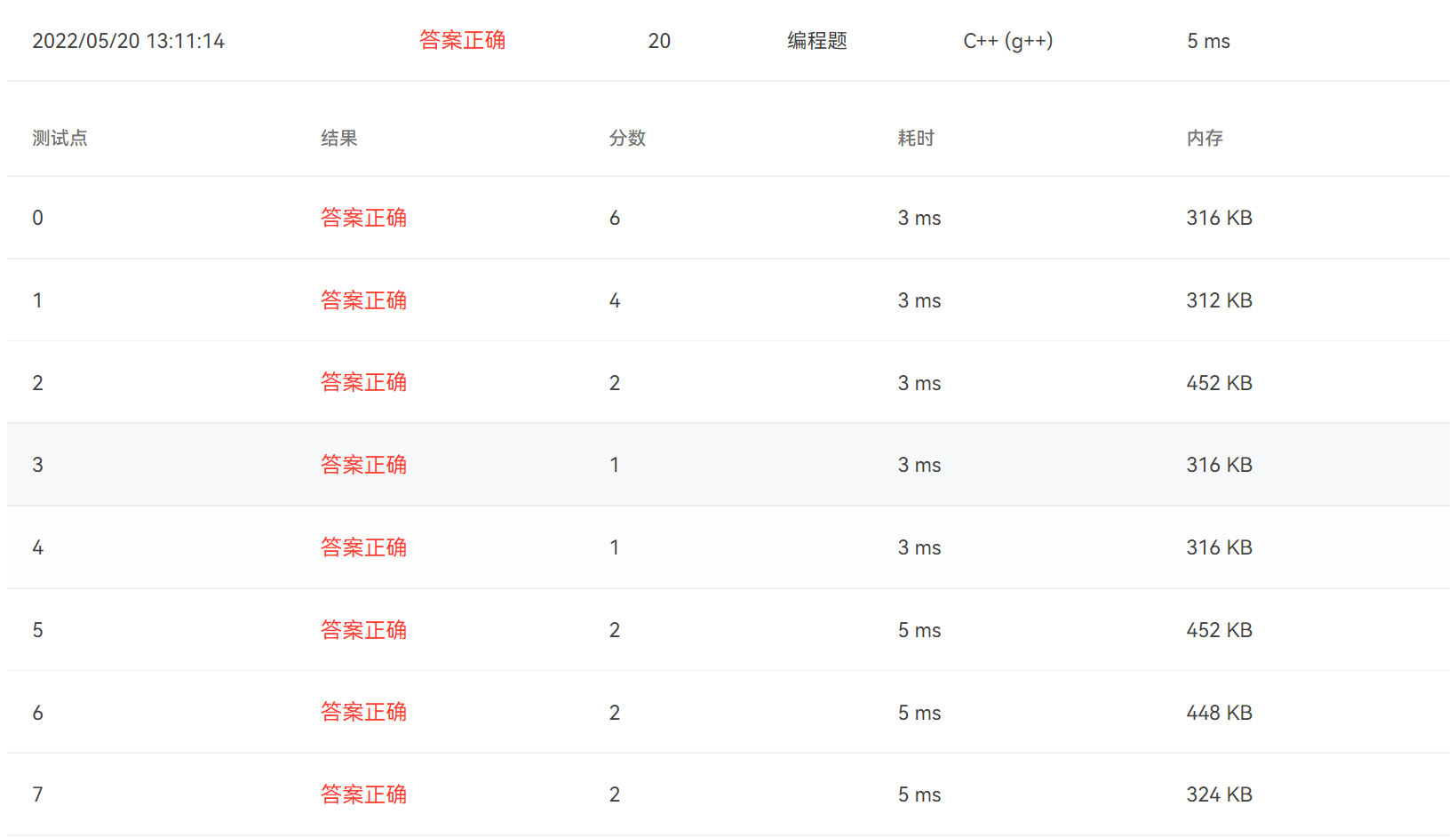
按照题目要求的方式记录根据规则选中的目标和实际的最佳目标。规则选中目标的方法:先从前r个人中选择最高分作为参考,然后从之后的嘉宾中选取第一个大于参考的作为牵手嘉宾(如果没有,牵手失败)。同时,遍历过程中要记录评分最高的嘉宾序号。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int r = int(1.0 * n / 2.718);
int pivot = -1; //参考标准
int maxSocre = -1; //最高评分
int select = 0, best; //选择的编号和最好的编号
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
if (i <= r)
pivot = max(pivot, tmp); //在前r个中找到参考
else {
if (select == 0 && tmp > pivot) { //如果没有选择,则选择比参考好的第一个
select = i;
}
}
if (tmp > maxSocre) { //计算最高分数
maxSocre = tmp;
best = i;
}
}
cout << select << " " << best; //输出结果
return 0;
}提交记录
7-7 新式六合彩
题目
思路
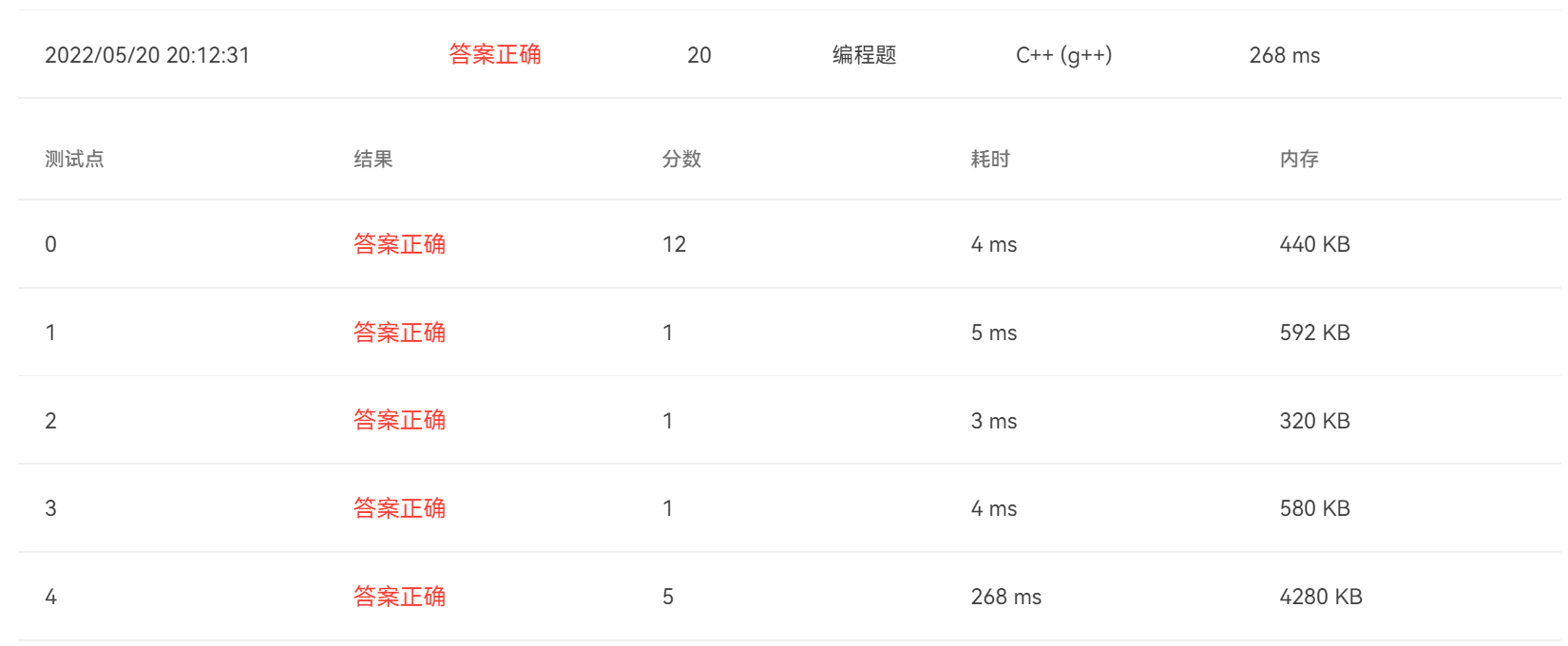
保存二维数组,然后遍历指定的幸运行和幸运列,选取和幸运数字最接近的位置。其中,题目要求比较范围是幸运行和幸运列中所有人;然后,因为只有可能行列交叉位置会重复,所以计算在幸运行中,在幸运列中直接跳过;最后,记得-1的位置一定要跳过(000000这个幸运数和-1很接近)。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m; //读入数据
vector<vector<int>> matrix(n, vector<int>(m, -1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> matrix[i][j];
}
}
int r, c, num;
cin >> r >> c >> num;
vector<pair<int, int>> sp;
//处理幸运行
int absPivot = INT_MAX; //不要用第一个进行初始化(可能第一个是-1),直接初始化成最大值
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (matrix[r - 1][i] == -1) //空位跳过
continue;
int absi = abs(matrix[r - 1][i] - num);
if (absi < absPivot) { //如果找到更接近的,清空
sp.clear();
absPivot = absi;
}
if (absi <= absPivot) { //不论是小于还是等于,都会加入一个坐标
sp.push_back({r, i + 1});
}
}
//处理列
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (matrix[i][c - 1] == -1 || i == r - 1) //空位和交叉点跳过
continue;
int absi = abs(matrix[i][c - 1] - num);
if (absi < absPivot) { //如果找到更接近的,清空
sp.clear();
absPivot = absi;
}
if (absi <= absPivot) { //不论是小于还是等于,都会加入一个坐标
sp.push_back({i + 1, c});
}
}
for (auto& item : sp) { //输出结果
printf("(%d:%d)\n", item.first, item.second);
}
return 0;
}
//测试点2 不过提交记录
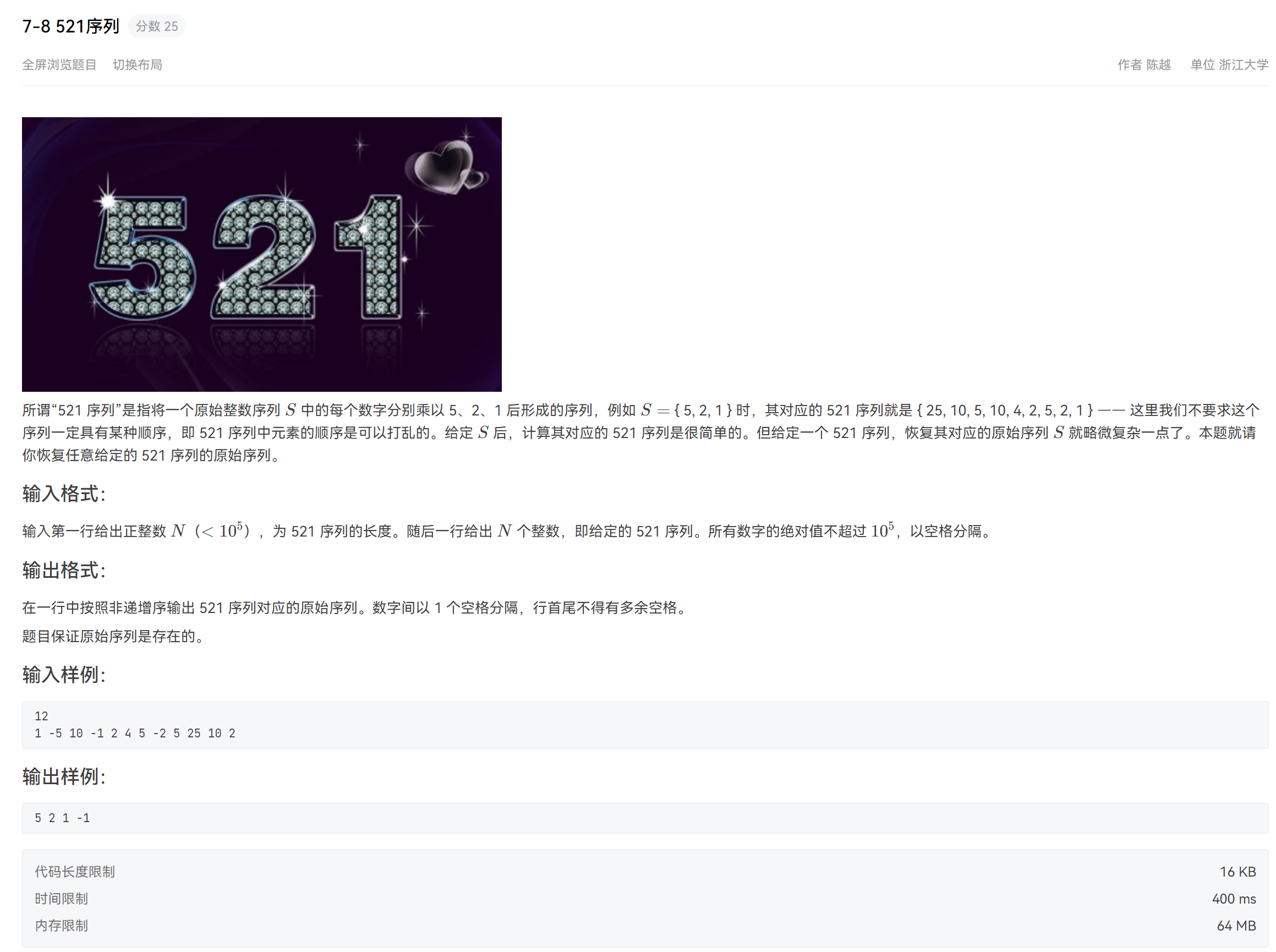
7-8 521序列
题目
思路
以正数为例,因为原始序列都分别乘以1、2、5构成“521”序列。那么如果从小到大遍历,每次序列中最小的数字便是原始序列中的数字×1的结果,去除其×2和×5的数字。然后继续重复此操作直到序列中没有数字为止,就可以获得最终的原始序列。这里需要强调一下几点:
(1)为何正数要从小到大遍历
因为从小到大处理,可以避免较小值的倍数混淆了原始序列中数字的个数。比如序列2 5 10 | 4 10 20 | 10 25 50,因为2和5的倍数会出现10,而10也在原始序列中,从小到大处理会在处理小数字2和5的时候削减他们倍乘之后数字10的计数。
(2)负数不能从小到大,而是按照绝对值从小到大处理。原因和(1)中解释的相同。
(3)代码的写法不同,对于0的处理可能不同,具体处理方法见代码。
题解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 100010;
int positive[MAXSIZE] = {0};
int negative[MAXSIZE] = {0};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> ans;
int positive_cnt = 0; //正负分开处理
int negative_cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
if (tmp >= 0) { //放入非负计数数组
positive[tmp]++;
positive_cnt++;
} else { //放入负数计数数组
negative[-tmp]++;
negative_cnt++;
}
}
positive_cnt /= 3, negative_cnt /= 3; //原始数据的个数是 总个数/3
int id = 0;
while (positive_cnt) { //必须从小到大遍历,否则会受到其他数字干扰,比如如果原始数字有2 5 10 那么2*5和5*2都会干扰10的计数
while (!positive[id]) id++; //找到下一个需要处理的数字
int cnt = positive[id];
if (id == 0) //如果是0,那么计数器需要/3,因为其倍数也是0,所以计数器相当于重复三次
cnt /= 3;
ans.insert(ans.end(), cnt, id); //cnt表示了原始序列中id的个数,插入到答案数组中
// 对于0的问题:可以每次减1,这样不用计算cnt,每次只处理一个数字即可
// 这里使用cnt是因为对于每个数字而言,从小到大遍历,由于不受干扰,计数便是其在原始序列中出现的次数,可以一次性处理完
positive[id] -= cnt; //倍数计数器减去对应个数,
positive[id * 2] -= cnt;
positive[id * 5] -= cnt;
positive_cnt -= cnt; //以此处理cnt个重复的数字,计数器-cnt
}
id = 0;
while (negative_cnt) { //负数处理办法类似
while (!negative[id]) id++;
int cnt = negative[id];
ans.insert(ans.end(), cnt, -id);
negative[id] -= cnt;
negative[id * 2] -= cnt;
negative[id * 5] -= cnt;
negative_cnt -= cnt;
}
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end()); //排序后输出
for (int i = ans.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i != ans.size() - 1)
putchar(' ');
cout << ans[i];
}
return 0;
}
提交记录
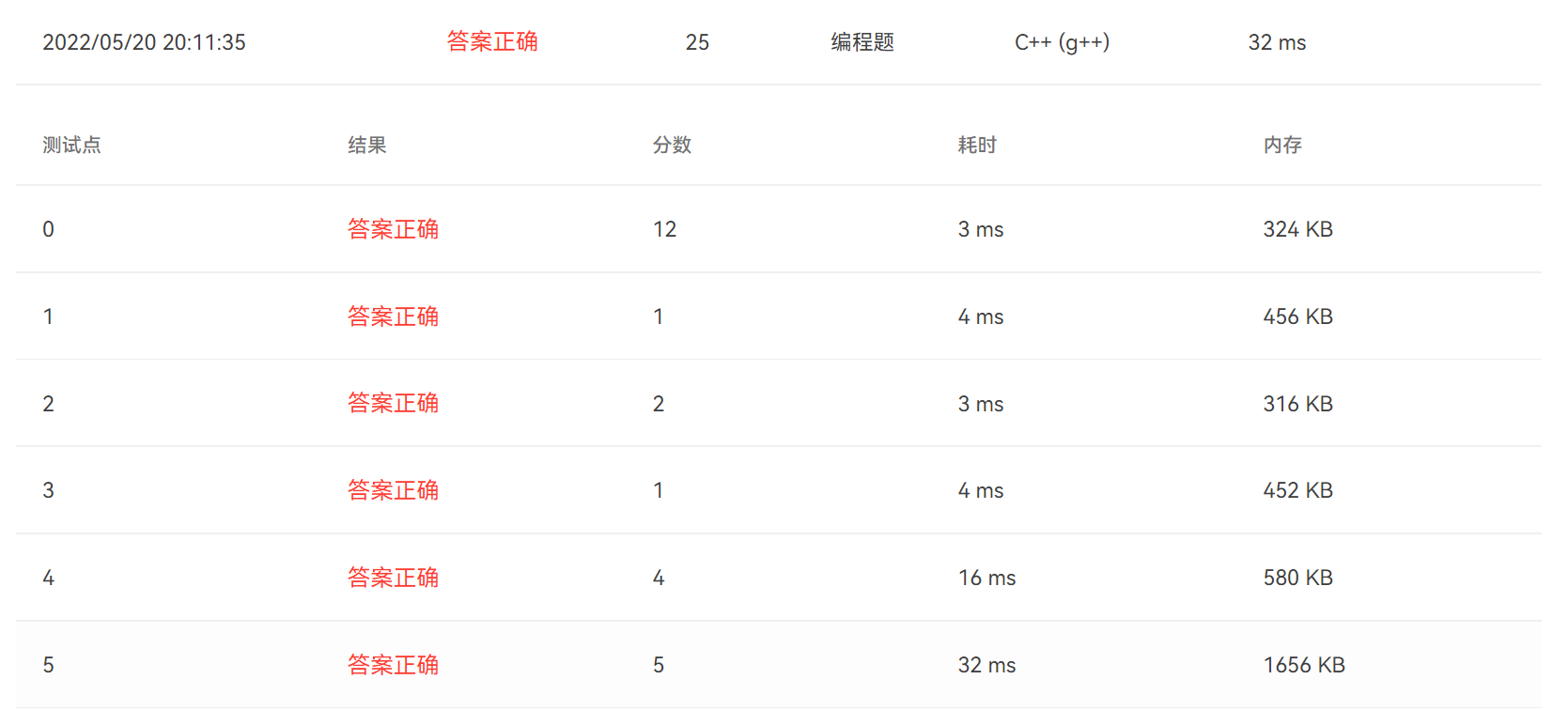
其他写法
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
map<int, int> cnt;
vector<int> a(n), r;
for (int &x : a) cin >> x, ++cnt[x];
sort(all(a), [&](int a, int b) { return abs(a) < abs(b); });
for (int x : a)
if (cnt[x])
r.push_back(x), --cnt[x], --cnt[x * 2], --cnt[x * 5];
sort(all(r));
reverse(all(r));
for (int i = 0; i < r.size(); i++) cout << r[i] << " \n"[i + 1 == r.size()];
}








Comments | NOTHING