OpenGL绘制球体
在本文中,我们将使用OpenGL绘制一个球体。这个过程中,本文会涉及到如何计算生成球体的顶点数据、顶点法线和纹理坐标等,并用这些数据绘制一个地球。
球体数据
OpenGL中的几何形体都是使用三角面表示的,球体也不例外。我们通过将球体分割成经纬网格,然后将每个网格进一步划分为三角形的方法得到所有的顶点和索引数据。
球体数据的表示
本文提供一个写好的球体类Ball,该类使用半径r和经纬两个方向的划分数量xSegNum和ySegNum作为构造参数,生成以(0,0,0)为球心的球体所有顶点、法线和纹理坐标。其中,定义二维和三维向量用于表示纹理坐标、顶点坐标和法向量。
源文件vec.h如下:
#pragma once
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
struct Vec2 {
Vec2(float x = 0.0, float y = 0.0) : x(x), y(y) {}
float x, y;
};
struct Vec3 {
Vec3(float x = 0.0, float y = 0.0, float z = 0.0) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
float x, y, z;
Vec3 normalize() const {
float len = sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);
assert(len != 0);
return Vec3{x / len, y / len, z / len};
}
};
struct Vertex {
Vec3 position;
Vec3 normal;
Vec2 texCoord;
};球体数据的生成
球体数据的生成思路如下:
根据构造的参数按照经纬进行网格划分,使用双层循环遍历划分的网格,计算网格的每一个顶点。如下图所示:

外层循环以经向为主,从0°到360°进行遍历,每次遍历一个经向的划分片;内层循循环以纬向为主,从-90°到90°进行遍历(为了方便生成纹理的uv坐标),每次遍历一个纬向的划分片。
在球体中,有了两个方向的角度,利用几何知识和三角函数就能很好地计算出每一个顶点的坐标,法线即为球心到顶点的向量,纹理坐标便是按照遍历的顺序的划分片序归一化后得到的值。在计算得到每一个顶点以后,同样地以双层循环遍历划分的网格,为每个网格生成三角面的顶点索引,遍历顺序和顶点生成的顺序一致。
球体类的声明和实现源文件ball.h如下:
#ifndef BALL_H
#define BALL_H
#include "vec.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
class Ball {
public:
Ball(float radius = 1.0f, int xSegNum = 180, int ySegNum = 180):
m_radius(radius), m_xSegNum(xSegNum), m_ySegNum(ySegNum){
generateData();
}
~Ball(){};
private:
void generateData(){
const float PI = static_cast<float>(3.141592653589793);
const float HalfPI = float(PI / 2.0);
float dYaw = 2.0f * PI / float(m_xSegNum);
float dPitch = PI / float(m_ySegNum);
for (int i = 0; i <= m_xSegNum; ++i) {
float yaw = i * dYaw;
float U = (float)i / (float)m_xSegNum;
for (int j = 0; j <= m_ySegNum; ++j) {
float pitch = -HalfPI + j * dPitch; // 为了正确计算UV坐标,维度从南极开始计算
float V = (float)j / (float)m_ySegNum;
float x = m_radius * cos(pitch) * cos(yaw);
float y = m_radius * cos(pitch) * sin(yaw);
float z = m_radius * sin(pitch);
Vertex vertex;
vertex.position = Vec3(x, y, z);
vertex.normal = vertex.position.normalize(); // 球体的法线就是从原点指向顶点的向量
vertex.texCoord = Vec2(U, V); // 纹理坐标可以直接用U和V
vertices.push_back(vertex);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m_xSegNum; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m_ySegNum; ++j) {
// 经纬网格面片的左下三角
indices.push_back(i * (m_ySegNum + 1) + j);
indices.push_back((i + 1) * (m_ySegNum + 1) + j);
indices.push_back(i * (m_ySegNum + 1) + j + 1);
// 经纬网格面片的右上三角
indices.push_back(i * (m_ySegNum + 1) + j + 1);
indices.push_back((i + 1) * (m_ySegNum + 1) + j);
indices.push_back((i + 1) * (m_ySegNum + 1) + j + 1);
}
}
}
public:
std::vector<Vertex> vertices;
std::vector<unsigned int> indices;
private:
float m_radius;
int m_xSegNum;
int m_ySegNum;
};
#endif
需要说明的是,我为了方便这个类的使用并没有对这个类进行严格的设计,比如,我没有添加const限定的读取接口而是直接把顶点和索引作为共有成员。另外,该类生成的球体数据本身也有可以优化的点,在本文中不做进一步讨论。
绘制球体
根据OpenGL教程,可以轻松地使用上述球体的数据进行球体的绘制,以下提供一种实现以验证数据的正确性。
着色器
本文的示例对球体数据的渲染只用到了最基础的顶点着色器和片元着色器。
其中,顶点着色器内容如下:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
}片段着色器内容如下:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.5, 0.31, 1.0);
}主函数
本文中根据LearnOpenGL教程,使用GLFW和GLAD创建OpenGL的环境,并且使用了教程中讲解教授的Shader类和Camera类,绘制的主程序源码如下:
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include <stb_image.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "shader.h"
#include "camera.h"
#include "ball.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 5.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // time between current frame and last frame
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// tell GLFW to capture our mouse
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// build and compile our shader zprogram
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("../shaders/drawball.vs", "../shaders/drawball.fs");
// set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
Ball ball(1.0, 30, 30);
auto && vertices = ball.vertices;
auto && indices = ball.indices;
unsigned int VBO, VAO, EBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(Vertex), vertices.data(), GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// position attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
// 绑定EBO
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(GLuint), indices.data(), GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// 开启线框模式
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
// render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// per-frame time logic
// --------------------
float currentFrame = static_cast<float>(glfwGetTime());
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// input
// -----
processInput(window);
// render
// ------
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// 绘制cube
ourShader.use();
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
ourShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
ourShader.setMat4("view", view);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
ourShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, static_cast<GLsizei>(indices.size()), GL_UNSIGNED_INT, (void*)0);
// glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
// optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &EBO);
// glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
bool isDoubleSpeed = false;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_LEFT_SHIFT) == GLFW_PRESS)
isDoubleSpeed = true;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse moves, this callback is called
// -------------------------------------------------------
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(static_cast<float>(yoffset));
} 开启线框模式后,绘制的效果如下:
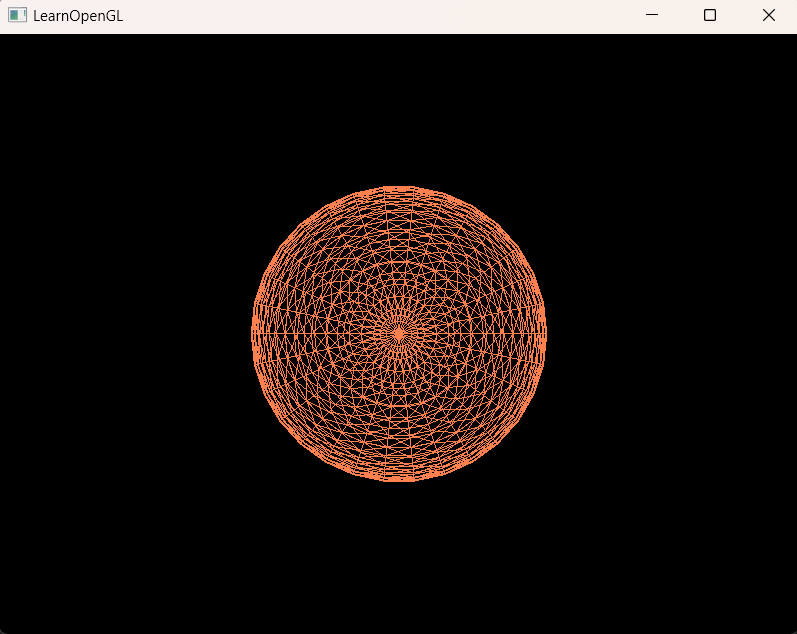
球体纹理
如果你已经学习过OpenGL纹理的相关知识了,那么就可以进一步利用纹理坐标为球体添加纹理图案。本文选取地球的图片作为纹理贴图,更多太阳系天体的贴图可以戳这里。
着色器
添加了纹理计算的顶点着色器和片段着色器略有不同。
其中,顶点着色器如下:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoord;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
out vec2 TexCoord;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
TexCoord = aTexCoord;
}片段着色器如下:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec2 TexCoord;
uniform sampler2D ourTexture;
void main()
{
FragColor = texture(ourTexture, TexCoord);
}主函数
学习过纹理的加载方法以后,以下的示例代码应该比较容易理解。在绘制前需要配置顶点属性中的纹理坐标,加载并绑定纹理。为了有更好的展示效果,我在这个示例中取消了窗口对鼠标的捕获,并且为Camera类新增了一个冻结的功能(使用标记控制不对相机参数进行计算)以保证观察的视口不会发生变化。示例代码如下所示:
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include <stb_image.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "shader.h"
#include "camera.h"
#include "ball.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 5.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // time between current frame and last frame
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
// 用于绑定纹理,第一个参数为纹理的ID,第二个参数为纹理文件的路径,第三个参数为纹理文件的类型(GL_RGB、GL_RGB_A等)
void bindTexture(unsigned int &texture, std::string fileName, GLenum picType){
glGenTextures(1, &texture);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture);
// 为当前绑定的纹理对象设置环绕、过滤方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
int width, height, nrChannels;
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true);
unsigned char* data = stbi_load(fileName.c_str(), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if(data){
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, picType, width, height, 0, picType, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
}
int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// tell GLFW to capture our mouse
// glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// build and compile our shader zprogram
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("../shaders/drawearth.vs", "../shaders/drawearth.fs");
// set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
Ball ball(1.0, 60, 60);
auto && vertices = ball.vertices;
auto && indices = ball.indices;
unsigned int VBO, VAO, EBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(Vertex), vertices.data(), GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// position attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// normal attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)sizeof(Vec3));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
// texture coordinate attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)(2 * sizeof(Vec3)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
// 绑定EBO
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(GLuint), indices.data(), GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// glBindVertexArray(0);
unsigned int texture;
bindTexture(texture, "../textures/earth.jpg", GL_RGB);
// 开启线框模式
// glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
camera.Freeze();
// render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// per-frame time logic
// --------------------
float currentFrame = static_cast<float>(glfwGetTime());
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// input
// -----
processInput(window);
// render
// ------
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// 绘制cube
ourShader.use();
int width, height;
glfwGetFramebufferSize(window, &width, &height);
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)width / (float)height, 0.1f, 100.0f);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
ourShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
ourShader.setMat4("view", view);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(-90.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
model = glm::rotate(model, float(glfwGetTime())*glm::radians(20.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f));
ourShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, static_cast<GLsizei>(indices.size()), GL_UNSIGNED_INT, (void*)0);
// glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
// optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &EBO);
// glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
bool isDoubleSpeed = false;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_LEFT_SHIFT) == GLFW_PRESS)
isDoubleSpeed = true;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime, isDoubleSpeed);
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse moves, this callback is called
// -------------------------------------------------------
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(static_cast<float>(yoffset));
} 最终,绘制出的地球效果如下:










Comments | 6 条评论
为什么不用你写的ShaderProgram类呢
@1030056861 因为,先有的绘制球体的代码,后来学到细分着色器和几何着色器才写了新的ShaderProgram类,绘制球体的代码没改直接用了。
Failed to load texture 请问一下为什么bindtextrure报这个错误,加载不了纹理
@hamu 是不是因为纹理文件不存在,格式不正确,或者路径不对?
@songjiahao 使用绝对路径以后解决了,但是相对路径和当前目录下还是不行
@hamu 假如.exe和texture.png在同一个目录下,load的时候路径直接填写texture.png就可以。如果你使用的是cmake等构建工具,检查一下生成的exe和纹理文件路径是否匹配。