VS Code设置C++代码风格
前置要求
需要在VS Code中安装C/C++扩展,因为其中自带了clang-format,可以实现自动格式化。只需做相应的配置即可自定义代码风格。
设置方法
配置格式化风格
VS Code在设置 > 扩展 > C/C++ > 格式设置中支持使用多种方式来定义格式化风格:
1.使用VS Code中预定义好的编码样式如:Visiual Stuido、LLVM、Google等;
2.使用file选项从当前目录或者工作区目录中的.clang-format文件加载样式;
3.使用file:<路径>/.clang-format来引用指定路径上的文件进行样式的加载;
4.使用{键:值,...}类似的形式指定文件样式;
四种方式任选其一即可,本文以第3种和第4种为例进行讲解。其中,本文推荐使用指定文件的方式进行编码风格配置,具有容易维护、便于分享等优点。如果不同工程中的代码风格要求有所不同,推荐使用file选项的配置方式。如果格式化风格样式的改动比较小,可以使用键值对的方式基于某一种编码风格进行快速配置。
使用特定文件指定风格
在文件 > 首选项 > 设置 > 扩展 > C/C++ > 格式设置中找到Clang_format_style选项,如下所示:
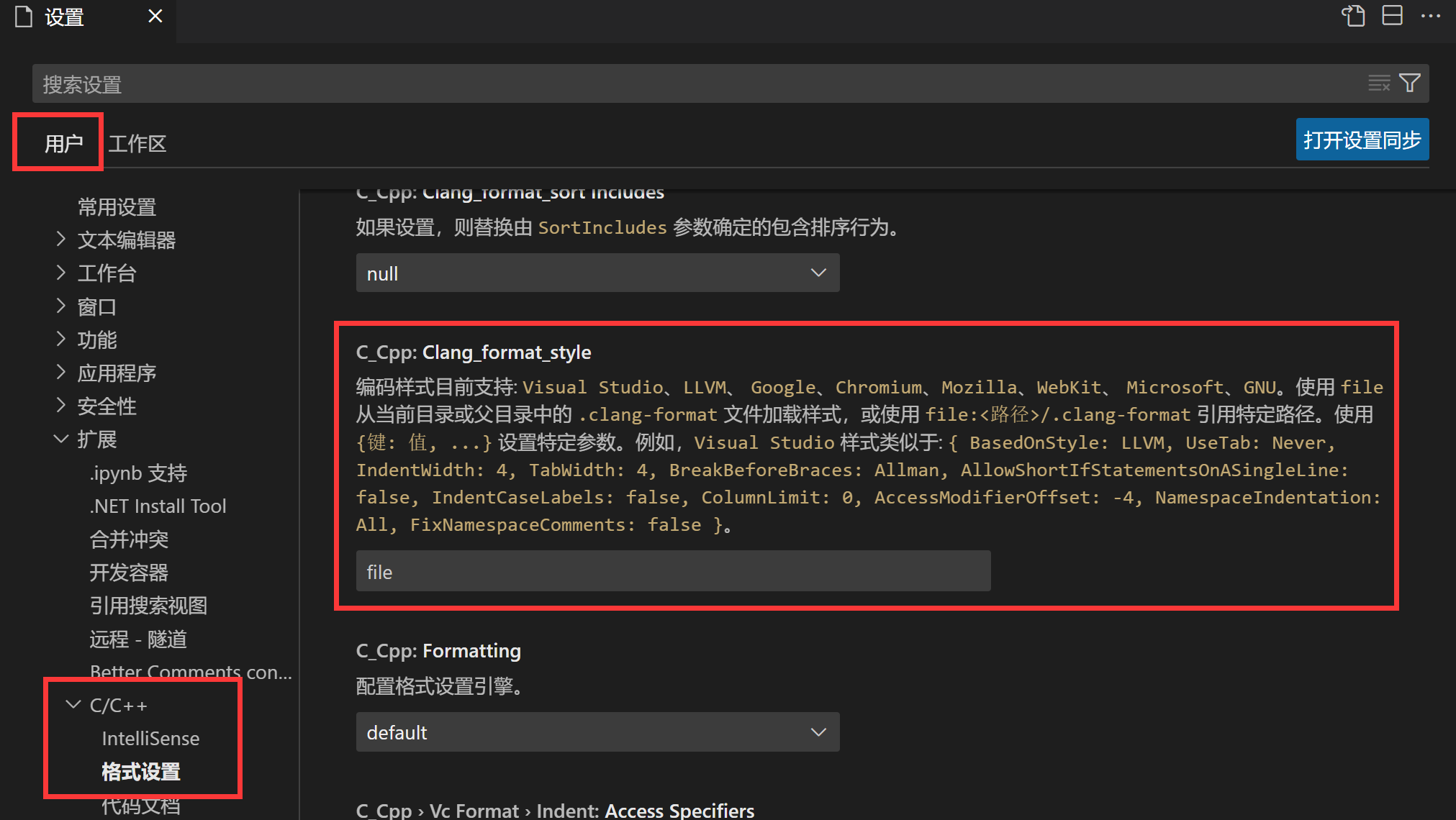
设置为file:<路径>/.clang-format,其中路径为自己的.clang-format文件所在的路径。文件内容可以根据clang-format的格式进行编写,示例如下所示:
BasedOnStyle: Google
UseTab: Never
IndentWidth: 4
TabWidth: 4
BreakBeforeBraces: Attach
AllowShortIfStatementsOnASingleLine: false
IndentCaseLabels: false
ColumnLimit: 80
AccessModifierOffset: -4
NamespaceIndentation: All这里的配置基于Google规范并额外自定义了一些配置项:使用了4个空格的缩进、左括号不换行、限制列数为80(即列数超过80,格式化时会自动换行)、public等访问权限修饰符缩进偏移以及命名空间内部缩进等。
使用键值对方式指定风格
可以直接使用{key:value,...}的方式来设定参数,类似于文件方式的配置项,但是表达格式略有不同,如下所示:
{ BasedOnStyle: Google, UseTab: Never, IndentWidth: 4, TabWidth: 4, BreakBeforeBraces: Attach, AllowShortIfStatementsOnASingleLine: false, IndentCaseLabels: false, ColumnLimit: 80, AccessModifierOffset: -4 }配置格式化触发方式
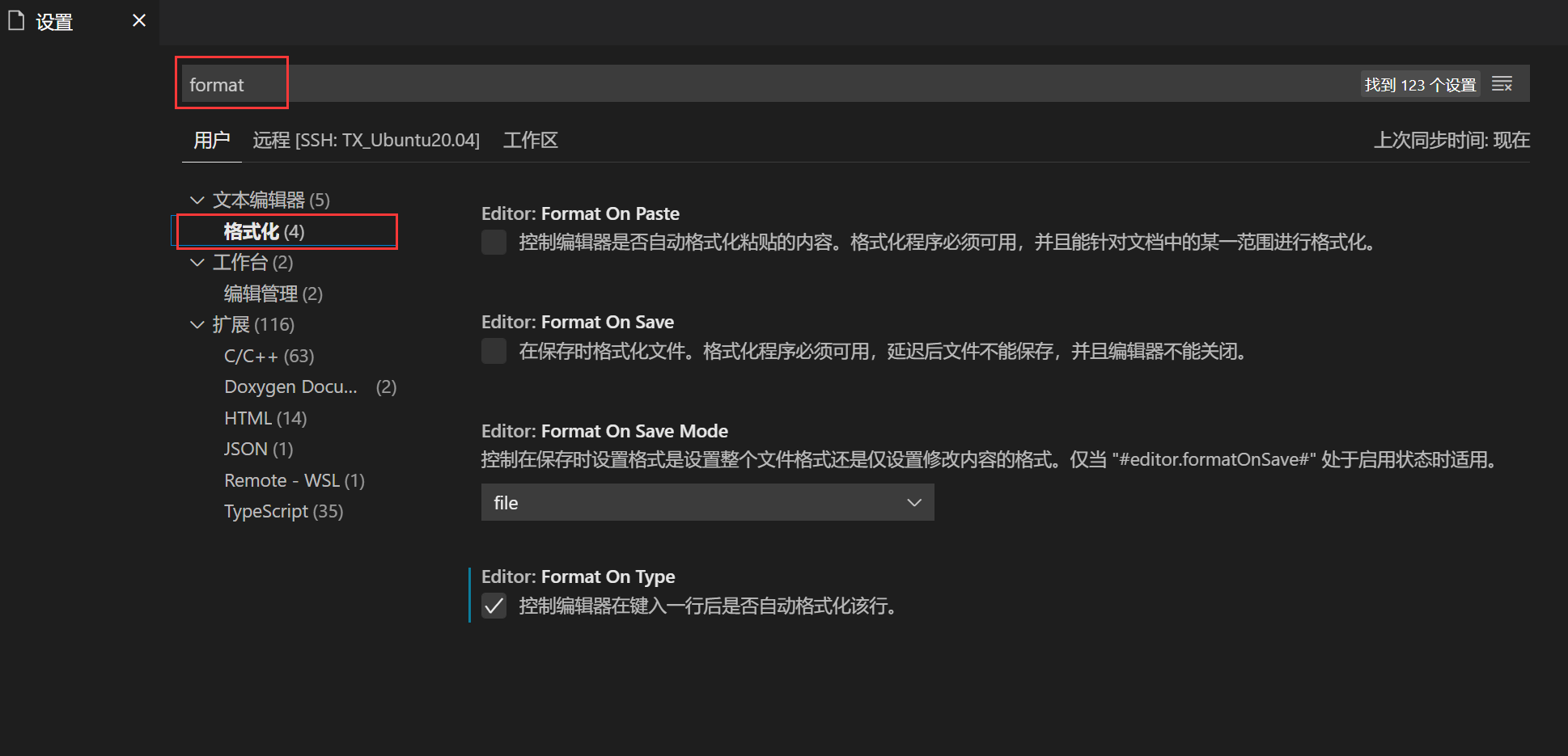
在文件 > 首选项 > 设置中搜索format,然后选中格式化,可以勾选格式化方式:粘贴后格式化,保存时格式化,键入一行后格式化。
格式化效果
这里展示一段格式化之后的效果:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <valarray>
//作为成员实现has-a关系
class Student {
private:
typedef std::valarray<double> ArrayDb;
std::string name;
ArrayDb scores;
std::ostream &arr_out(std::ostream &os) const; //输出array中的元素
public:
Student() : name("Null Student"), scores() {}
explicit Student(const std::string &s)
: name(s), scores() {} //禁止隐式转换
explicit Student(int n) : name("Nully"), scores(n) {}
Student(const std::string &s, const ArrayDb &a) : name(s), scores(a) {}
Student(const char *str, const double *pd, int n)
: name(str), scores(pd, n) {}
~Student() {}
double Average() const;
const std::string &Name() const;
double &operator[](int i);
double operator[](int i) const;
//友元
friend std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &is, Student &stu);
friend std::istream &getline(std::istream &is, Student &stu);
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Student &stu);
};
double Student::Average() const {
if (scores.size() > 0)
return scores.sum() / scores.size();
else
return 0;
}
const std::string &Student::Name() const { return name; }
double &Student::operator[](int i) { return scores[i]; }
std::ostream &Student::arr_out(std::ostream &os) const {
int i;
int lim = scores.size();
if (lim > 0) {
for (i = 0; i < lim; i++) {
os << scores[i] << " ";
if (i % 5 == 4)
os << std::endl;
}
if (i % 5 != 0)
os << std::endl;
} else
os << " empty array ";
return os;
}
double Student::operator[](int i) const { return scores[i]; }
std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &is, Student &stu) {
is >> stu.name;
return is;
}
std::istream &getline(std::istream &is, Student &stu) {
getline(is, stu.name);
return is;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Student &stu) {
os << "Scores for " << stu.name << ":\n";
stu.arr_out(os);
return os;
}
void set(Student &sa, int n);
const int pupils = 3;
const int quizzes = 5;
int main() {
using namespace std;
Student ada[pupils] = {Student(quizzes), Student(quizzes),
Student(quizzes)};
int i;
for (i = 0; i < pupils; i++) set(ada[i], quizzes);
cout << "\nStudent List:\n";
for (i = 0; i < pupils; i++) cout << ada[i].Name() << endl;
cout << "\nResults:";
for (i = 0; i < pupils; i++) {
cout << endl << ada[i];
cout << "average: " << ada[i].Average() << endl;
}
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}
void set(Student &sa, int n) {
std::cout << "Please enter the sutdent's name: ";
getline(std::cin, sa);
std::cout << "Please enter " << n << " quiz scores:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) std::cin >> sa[i];
while (std::cin.get() != '\n') continue;
}








Comments | NOTHING